EXCISION OF CUTANEOUS LESION
There are a number of cutaneous diseases the treatment of wich is surgical, and the malignant or benign tumours of the skin belong to them. Their treatment consists of-primarily-the excision of the alteration. It is the task of the dermatologist to establish the diagnosis and the operation indication. We carry out the excision in our institute keeping the oncological and plastic principles strictly. Every removed alteration comes to histological examination, which decides whether the patient needs any further treatment.
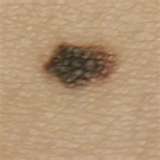
EXCISION OF ALTERATIONS UNDER THE SKIN
To establish a diagnosis about the palpable subcutaneous nodules which cause annoying and growing complaints, is a difficult task. The operation can be suggested by the surgeon or the dermatologist. The alterations are mostly lipomas, fibromas or different types of cysts. Their removal takes place generally in local anaesthesia. Good cosmetic results can be reached with suitable surgical technics besides the complete recovery. Histological examination is compulsory even here.
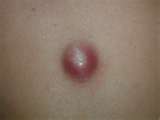
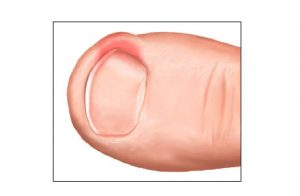
INGROWN NAIL
We call this alteration an ingrown nail, when the edge of the nail grows into the surrounding skin. Its induction is helped by the incorrect nail-cutting, wearing tight shoes, or not satisfactory hand and foot hygiene. The surroundings of the nail become red, swells, there is secretion and considerable pain. It becomes easily infected without treatment. The conservative treatment is generally unsuccessful. The solution is sugical. We use the Emmert-plasty in our clinic which ensures the best result. The essence of the operation is the wedgewise excision of the extreme quarter of the nail together with the granular tissue and the nail bed. The intervention is painless in an Oberst-type anaesthesia.
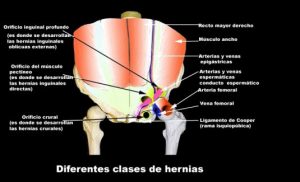
INGUINAL HERNIA
Inguinal hernia is the pathological condition when viscera get out of the abdominal cavitiy through a lumbar area of the abdominal wall, the so-called hernial ovifice into the thumb-stall like protrusion of the peritoneum, the hernial sac. Lumbar hernias constitute 80 % of all the hernias. In the case of inguinal hernia we distinguish direct and indirect hernia, depending of the fact where the inside ovifice from the abdominal cavity of the hervial ring can be found.
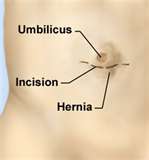
UMBILICAL HERNIA
The umbilical ring shuts in the first weeks after birth and its place is filled with scar-tissue directly under the skin. If the shutting doesn’t happen or the scar-tissue is feeble, hernia can develop.
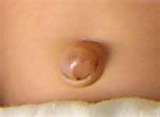
Treatment: The recognized and uncomplicated hernia constitute a relative surgical suggestion. The strangulated hernia means an absolute surgical indication.
The medical treatment of a hernia is only in a surgical way possible. We do the operation in local, spiral anaesthesia or general anaesthesia.
Surgical solutions: Reconstruction is all the abdominal and inguinal hernia can take place in two ways:
- With a direct closing of the hernial ovifice (sutura) or
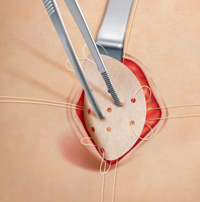
- With the implantation of a tissue-friend plastic net, and this tensefree solution diminishes the pain after the operation and the recurrence is a lot rarer.
Period after the operation: After operations carried out in a chosen point of time and if they are uncomplicated observation and treatment are unnecessary, at most alleviation. Suture removal takes place only a week later. Gradual replacement of loading is two months in case of traditional operations, in net implantation it can begin two weeks later.
Possible complications: No doctor can guarantee the harmlessness of an intervention absolutely. The serious operational complications are rare with the operations of abdominal hernia, but they cancan eevolve (injury of an organ, a nerve a blood vessel, secondary haemorrhage.) The danger is greater if the hernia is strangulated, especially if there has been a longer period after the stragulation. Greater overweight makes the job of the surgeon more difficult. The recurrence of the hernia can happen even after an effective and well-done operation. The frequency of the recurrence depends greatly of the fact if the patient keeps the instruction of the doctor.
PHELEBECTOMY
Venous disease appears most often on the lower limbs but it can occur in other parts of the body. These alterations can strike 25-30 % of the population of whon 15 % need medical treatment the greatest part of which can be done even ambulant if the patient sees the doctor in time.
The vein of a leg can be divided into deep and surface ones. Both nets can have acute and chronic diseases. In our clinic we treat the chronic diseases of the surface veins, i.e. with classical concept of the varicose vein.
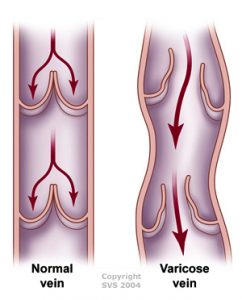
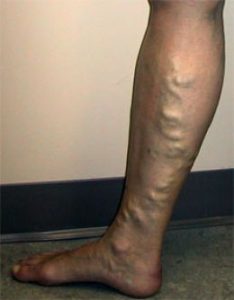
Its forms of appearence:
- Trunk variocisity
- The variocisity of the perforating (connecting) veins
- Branch variocisity
- Reticular (network) phlebectasia
- Broomlike phlebectasias
The exact judgement of the alterations can be done with physical examination or with different non-invasive examining methods (cloppler sonography, coloured duplex scan)
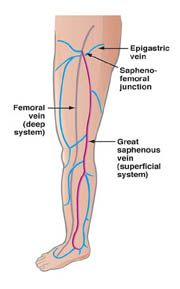
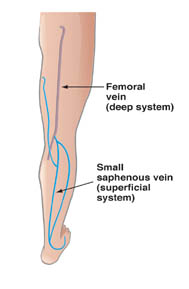
After the examinaton we decide about the suggested treatment, which is generally operation in the first two cases, by branch variocisity even sclerotherapy can be a suitable method besides the operation. In case of reticular or broomlike varicosity even the injection method is the therapy to be chosen.
In case of the concern of the whole vein stem we do the standard surgical intervention (crosstectomis, stripping) in general anaesthesia.
The mobilization of the patient begins even on the day of the operation. We can send home after a day’s observation and in case of no complaint and no symptoms. Compression bandage or elastic stockings are recommended for 6 weeks, with regular chekings.
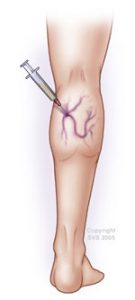
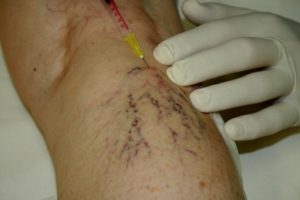
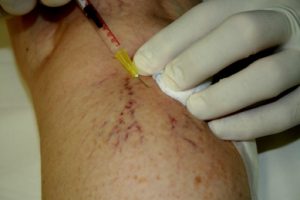
INJECTIONAL TREATMENT OF THE VEINS (SCLEROTHERAPY)
We do the treatment of branch-, reticular (network) and broomvein varicosity with this method, but the so-called foam sclerotizity is today a proved therapic method in all the appearing form of varicosity. The inside wall of the vein sustains an injury under the effect of the material put intothe vein with a syringe. The lacerated vein walls stick together due to compression, they become scarred tissues, a part of which is absorbed later on. After the treatment we put a compression bandage on the limb which must be worn for 1-6 weeks, depending on the thickness of the treated vein.
GYNECOMASTIA
The one or bilateral hypertrophy of the male mammary gland is called gynecomastia.Su
Surgical indication: examination, after stopping the exogen and endogen causes the gland plethora may cause complaints.
Surgical anaesthesia: local anaesthesia or narcosis.
Surgical method: subcutan mastectomy. We carry out the intervention ambulant or the frame of one-day-surgery.
